It is impossible to imagine an active and healthy lifestyle without movement. Joints are the most important elements of the musculoskeletal system, which allow a person to move freely and feel full. With age, dystrophic changes occur in bone and cartilaginous tissues, pain arises, which signals the onset of the disease.
The hip joint can withstand enormous loads throughout life, so it is not surprising that the most common pathology of ODA is arthrosis-arthritis of the hip joint. With this article, you will learn what it is, as well as the causes, consequences and methods of treating coxarthrosis.
Characteristics and causes of the occurrence
Coxarthrosis is a chronic inflammatory process of the hip joint, in which the cartilage tissue undergoes premature destruction.
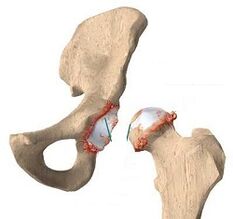
The development of the disease causes the proliferation of osteophytes and fusion of the acetabulum and head of the femur, which narrows the joint space, the joint loses its functionality.
Let's clarify that coxarthrosis is the same as osteoarthritis and deforming pelvic joint osteoarthritis.
The disease can arise as a primary pathology or develop in the context of existing diseases.
Let's consider the main causes of coxarthrosis:
- during active or excessive physical exertion (trauma, microtrauma, overload);
- congenital anomalies (dysplasia, Perthes' disease, primary joint deformity);
- inflammation of the pelvic bone (ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis);
- severe stress (spasm of blood vessels and muscles, aseptic necrosis, hypothermia);
- hormonal disorders;
- ischemic heart disease;
- diseases of the endocrine system (obesity, diabetes mellitus).
A complex of health problems leads to the development of coxarthrosis. Most of the time, the disease is diagnosed in middle and old people, however, in the presence of several triggering factors at the same time, young people and even children are susceptible to coxarthrosis.
Symptoms
In order to respond with time to the development of the pathology, it is important to observe the characteristic symptoms that change as the osteoarthritis progresses.
The first and most important symptom is pain in the leg, which penetrates the groin, gluteal muscles, sacrum, thigh and knee. The pain increases after physical effort, with prolonged maintenance of the standing and sitting position.
Important! At first, the pain may be mild and not appear in the pelvis, but, for example, in the knee. This fact hampers early diagnosis and correct diagnosis.

If the disease is not diagnosed in time, the patient will experience symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint such as:
- severe pain in the groin when walking or resting on the leg;
- painful and rough clicking when moving the hip to the side and walking (not to be confused with the click, which is inherent to most healthy people);
- joint stiffness, limitation of leg mobility;
- gait change, lameness, duck gait;
- shortening or stretching of limbs; muscular atrophy
- ;
- fixation of the leg in one position (ankylosis).
An important diagnostic sign of coxarthrosis is physical limitations when leaning forward, abducting the hip to the side.
A patient with this diagnosis has difficulty tying the shoelace on his own, sitting with his legs apart and sitting down deeply.
There are 3 degrees of osteoarthritis of the acetabulum and femoral head, which are characterized by the gradual destruction of the joint. We will consider your features below.
Stage 1 coxarthrosis is characterized by a slight destruction of the cartilage, the joint space is slightly narrowed.
In the second stage, the destruction of the cartilaginous tissue increases visibly, the first signs of the disease start to disturb: pain, stiffness.
Most severe damage to the hip joint occurs in 3 stages. It is characterized by profound destruction of the cartilage, bone deformation, pain at rest. The disease completely destroys the cartilage and deforms the femur.
The joint loses mobility, the leg is fixed and serves as a support. In this case, conservative therapy is impotent, requiring surgical treatment with joint replacement.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the disease shows how cartilage is affected and whether arthrosis of the hip joint can be healed.
The success of the therapy depends on when the treatment was started.
Note. The last stage of coxarthrosis does not respond to conservative therapy and requires surgical intervention. Diagnosing and treating the disease at the onset of the disease increases the chances of recovery.
To make the diagnosis, an external exam is performed, the degree of mobility of the hip joint is evaluated, the changes in gait and in the length of the legs. X-rays, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed to confirm primary coxarthrosis. If the patient requires surgical treatment, urine, feces, blood and joint fluid are removed in addition.
Treatment of the disease
Coxarthrosis is a progressive disease. It is impossible to cure it once, such as acute respiratory infections, and to forget the condition of your joints.
Successful treatment of grade 1, 2, and 3 deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint requires an integrated approach that combines therapeutic exercises, medications, physical therapy, and changes in the patient's lifestyle.
In extreme cases, the patient will need to resort to surgical treatment of coxarthrosis. The method of therapy depends on the degree of the disease.
Medicines
The first thing a patient diagnosed with osteoarthritis is prescribed is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers. They act directly at the site of inflammation and provide symptomatic treatment.
Note! It is important to observe the dosage and the duration of the course indicated by the doctor. The uncontrolled use of NSAIDs leads to side effects.
For the treatment of coxarthrosis, vasodilators are also prescribed. They are needed to increase blood flow to the diseased joint, to strengthen cartilage nutrition.
Chondroprotectors are used to restore cartilage tissue and joint mobility. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate are substances that stimulate the production of new building cells and inhibit the action of enzymes that destroy cartilage tissue.
Massage
Manual therapy or rehabilitation massage is passive gymnastics for the affected joints. Thanks to massage movements, blood circulation and lymphatic drainage are improved, muscles are strengthened, ligaments and tendons become more elastic. This approach to treatment helps to reduce pain, increases the effect of drug therapy and reduces the need for medication.
Important! The massage should only be performed by a qualified professional. Careless movements will cause even more pain and injury to the joint.
Physiotherapy exercises
Movement is the basis of life. Gymnastics for osteoarthritis of the hip bones aims to restore cartilage nutrition and joint mobility, strengthening the muscle corset.
Regular corrective gymnastics leads to less discomfort in the legs when walking.
Gymnastics allows you to treat your hip pain at home.
All movements are directed to the treatment and prevention of stages 1 and 2 of osteoarthritis of the hip joints.
Before starting the exercise, make sure that there are no contraindications for the exercises:
- hypertension
- ;
- critical days;
- infectious diseases;
- increased body temperature;
- the recovery period after surgery on Organs abdominal and thoracic organs;
- inguinal and umbilical hernia;
- intervertebral discs with hernia;
- acute inflammatory processes of internal organs or exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- serious diseases of the cardiovascular and circulatory system.
If any movement causes acute pain during exercise, it probably doesn't suit you, so it's best not to do it and exclude it from the complex.
Diet
Diet therapy for osteoarthritis of the hip joints aims to reduce and maintain normal weight.
Excess weight increases stress on the spine and joints, creating an additional risk of developing diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The basis of the diet is a moderate intake of foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Food must be whole and contain the necessary building blocks of cells: proteins, carbohydrates, fats.
Vegetable foods should be preferred: nuts, seeds, leafy vegetables, seasonal vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish, medium-fat fermented dairy products, vegetables and cereals.
Cow's milk should be consumed in moderation.
Greasy, spicy, smoked, canned, fried, canned dishes, semi-finished products, alcohol, coffee should be excluded from the diet.
Bad habits (smoking, drug addiction, overeating) will also have to be eradicated from your lifestyle, as they wear down your body, exposing you to premature aging.
How to get rid of pain with folk remedies
Homeopathy for coxarthrosis of the hip joint is one of the alternative therapy methods. Based on natural components, homeopaths create medicines for the treatment of pathologies of internal organs and the human skeleton. The peculiarity of homeopathic preparations for arthrosis is that they are able to restore the balance between the destruction of the cartilage by enzymes and the renewal of its tissues.
Attention! Before treating your hip joint at home, you need to undergo a diagnosis of the disease. It is important not to allow the pathology to worsen, as this can cost the person the ability to walk.

Homeopathic remedies, injections and ointments for the treatment of joints are selected based on the physical conditions of the environment and the location of the disease.
Before using any medication, you must consult a doctor!
Prevention
People predisposed to this pathology should avoid stress, injury, treat infectious diseases in time, exercise regularly, eat well and get enough sleep.
If you experience discomfort in your legs, it is recommended to contact an orthopedist immediately for diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis of the hip joints usually affects people over 45, athletes and children with congenital limb pathologies. The disease destroys and deforms the joint, the person feels terrible pain in the legs. Successful treatment of coxarthrosis requires the inclusion of therapeutic exercises, medication, correction of the patient's lifestyle and weight and manual therapy.
Health care is the key to longevity of the joints! Do not postpone the orthopedic consultation to the first symptoms of the disease.












































